The Shadow economy is the result of an insufficient level of development of economic relations in society and mechanisms of government administration.
Essence, types, forms of the shadow economy
The desire to hide income (or part of it) from regulatory authorities is present among many business entities and citizens around the world.
But in some countries there are favorable conditions for the prosperity of shadow business (massive corruption, weak management and control systems, inflated rates of taxes and fees), in others such conditions are suppressed by a strict system of punishments, the absence of systemic bribery, and a flexible, reasonable taxation system.
Another important factor in the development of the shadow economy is the difficult social situation. A person who lacks basic means of subsistence is forced to agree to work unofficially for a dishonest employer.
The main types and components of shadow activities from statistical and regulatory authorities:
- “Second” economy. Concealing part of the business transactions, trade turnover and finances. Carrying out officially permitted types of economic activities, business entities do not reflect in accounting, statistical, tax accounting and reporting a certain share of shipped products and services performed, and hide part of the revenue and real wages from taxation;
- “Black” business Illegal engagement in prohibited activities (smuggling, drug trafficking, hidden trafficking in counterfeit alcohol and tobacco products, sale of weapons);
- “Gray” economy Obtaining income through fraudulent means (cheating customers at places of trade, registration, theft, bribes), organizing underground workshops. Concealment from accounting of labor resources, their real salary and mandatory contributions to social funds and the budget. Questionable financial transactions for the purpose of withdrawing funds to offshore zones;
- Corruption income in the public sector (bribes for “resolving issues” to officials, representatives of regulatory authorities, as well as in the fields of healthcare, education, utilities and government services).
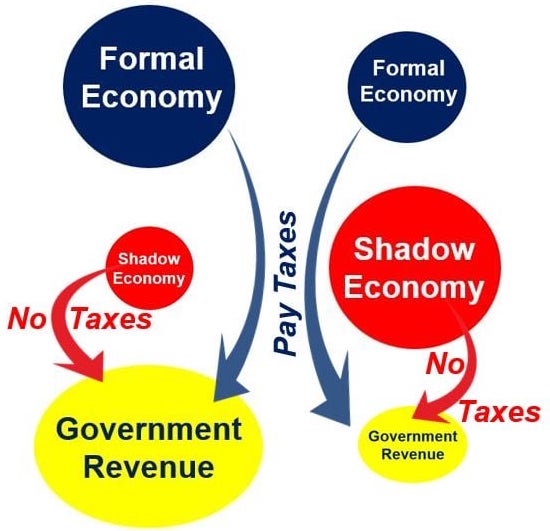
Fertile ground for “black” business is fueled by corruption in law enforcement agencies, the relationship between the shadow economy and organized crime. These two negative factors require government officials to carry out a principled and merciless fight and apply severe penalties to protect the country’s economy from destruction.
It is possible to indirectly influence the “gray” and “second” (or “white-collar”) economies using financial leverage. It should become unprofitable for business entities to risk their business for the sake of concealing taxes with a corresponding reduction in the tax burden, improvement in economic indicators, and the business atmosphere in the country.
Signs of the shadow economy
The main indicators highlighting the scale of the shadow economy on the territory of the state are:
- discrepancy between the level of actual consumption and official income;
- inflated demand for money compared to the methodological calculations of the central banks of countries;
- divergence in the consumption of electricity and other necessary resources used in production activities and the service sector;
- discrepancy between statistical indicators of employment and their size, established through sample observations and sociological surveys of the population.
Significant deviations in indicators indicate a large share of concealment from the state of transactions between entrepreneurs and an underestimation of the real level of income.
Causes of the shadow economy
An irrational system of taxes and fees, total supervision and control, and systemic corruption do not allow honest entrepreneurs to successfully compete with dishonest people and lead to a significant increase in the share of the shadow economy in the creation of the total gross product in the country.
Another reason for part of the economy to go into the shadows is financial crises, rising unemployment, and inflation.
A serious social factor dangerous for preserving the integrity of the state is the loss of trust of its citizens in government bodies. If people feel that government representatives, while collecting taxes, are not properly providing decent social services in the field of medicine, education, public services, and are not developing the economic sphere, they lose the desire to pay contributions to the state budget.
The discrepancy between economic and legal regulations and the real situation in the country also significantly affects the level of development of the shadow economy.
Growth of the shadow economy, its negative or positive impact
A striking example of the growth of the “shadow” is the nineties of the last century in the post-Soviet space. There was no new legislative framework, no clear structure of law enforcement agencies, and real power in many places passed to organized crime actors.
The negative consequences of the shadow economy are expressed in the state’s failure to receive the necessary funds to fill budgets at all levels, the loss of the ability to timely fulfill its obligations to residents in the social sphere (payment of pensions, benefits, ensuring an adequate level of healthcare, education).
Ultimately, when the country is actually ruled by gangster groups based on the accumulation of huge shadow capital, official power structures completely lose their purpose in foreign and domestic policy, which leads to the destruction of public administration.
At the same time, during periods of financial crises, the “white-collar” and “gray” types of the shadow sector of the economy partially contribute to the preservation of business entities. Preserving hidden jobs and unaccounted income allows them to survive in difficult financial conditions, which would become impossible if obligations to the state budget were fully fulfilled.
Methods for assessing the shadow economy
Scientists from many countries have studied the main influencing factors and developed methods for determining the size of the economic “shadow”.
Direct methods are based on the analysis of information obtained through special surveys, observations, and audits in the area of income and expenses of business entities, able-bodied citizens and their actual employment.
Indirect methods include a thorough analysis of discrepancies in calculated and actual data on commodity flows and the consumption of main types of production resources.
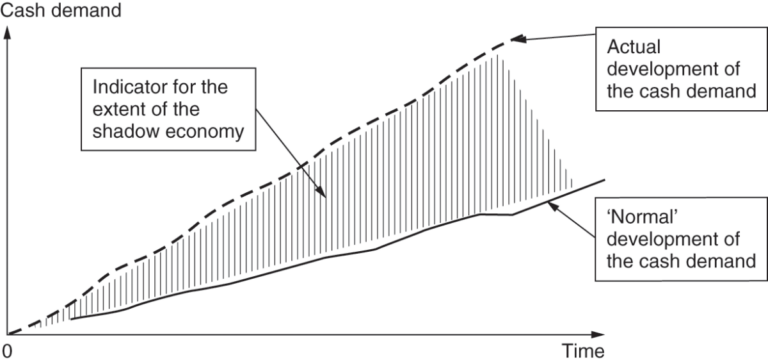
Monetary methods are based on comparison and analysis of the use of cash in circulation.
Structural methods are aimed at studying the share of hidden turnover in the main areas of the shadow economy.
Shadow economy in different countries of the world
The main reason for this negative fact is weakness, insufficient development of public administration, mass reluctance to comply with legal norms and actually combat corruption:
- In Russia and Armenia, the share of shadow income amounted to 45%, shadow labor costs 40%;
- In Azerbaijan, 60 and 50%, respectively;
- In Ukraine, 50% of GDP and 41% of labor resources are in the shadow.
In the countries of Central and Eastern Europe with a stable state and economic system, the level of shadow GDP averaged 29%, labor employment “in the shadow” – 23%. In the USA, the “shadow” is, according to various estimates, up to 10%, in Germany and Great Britain – 12%.
When determining the size of shadow business transactions in Russia in the 90s of last year, the “Italian system” of calculations was used, based on determining the shadow employment of able-bodied citizens.
Interesting facts about the shadow economy
- Calculated indicators for hidden economic turnover in Russia indicate a gradual decrease in the share of the “shadow” in the total GDP to 25-30%. But at the same time, the level of corruption does not fall. Probably, the modern government apparatus is not committed to a real fight against corruption.
- Calculations and banking information indicate the annual dubious withdrawal of up to 30 billion dollars of financial resources from Russia. Russia’s total GDP in 2016 was 1.28 trillion. dollars.
- In a prosperous US economy, the amount of “shadow” is 10 percent of GDP. But in absolute terms, this is a huge figure of more than 2 trillion. dollars!