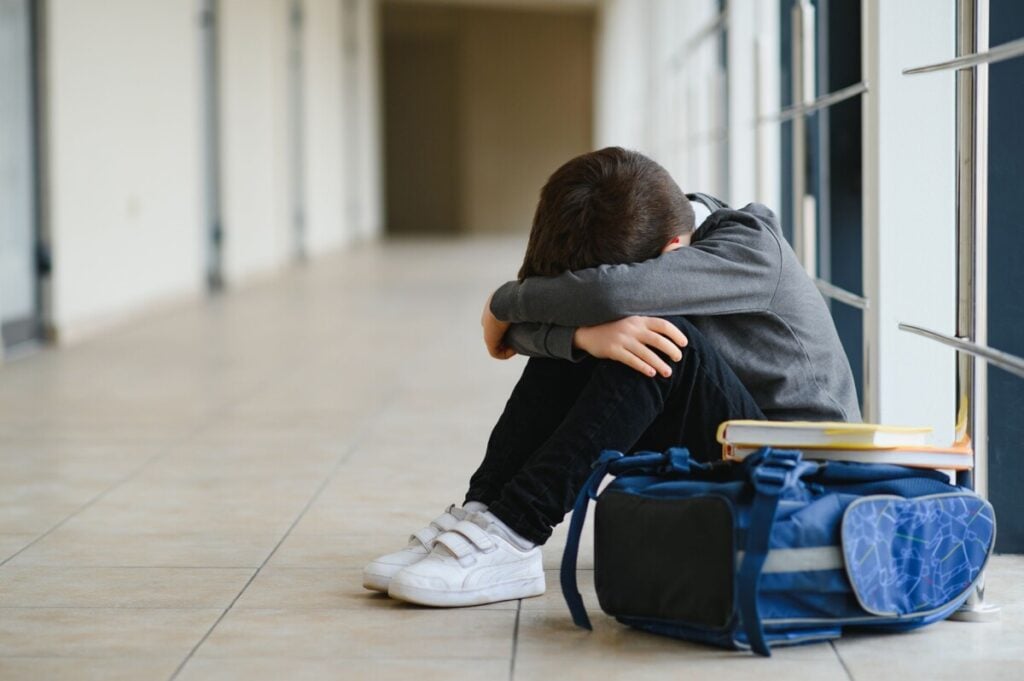
Bullying – means intimidation, harassment, mockery. It can be defined as the intention to intimidate a person and expose him to situations that make him tense, afraid and fearful.
- What behavior can be considered bullying?
- Bullying at school - how does it manifest itself?
- How can you tell if a child is being bullied?
- Bullying at school - who is the culprit and who is the victim?
- Victims of bullying - why are they bullied?
- Victim of bullying - how can family help?
- Where should I go for help in case of bullying?
Currently, this term is increasingly applied to situations involving aggression on school grounds among students and peers.
There are three characteristics that help determine whether a particular situation of aggression from peers can be considered bullying:
- Intentionality, i.e. the fact that the offender commits negative actions intentionally.
- Repetition, that is, prolonged actions by the offender and repeated acts of aggression against the same victim.
- Power imbalance between perpetrator and victim.
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of cases of bullying in the school environment. Such violent acts have a very strong negative impact on the lives of children, young people and adults.
What behavior can be considered bullying?
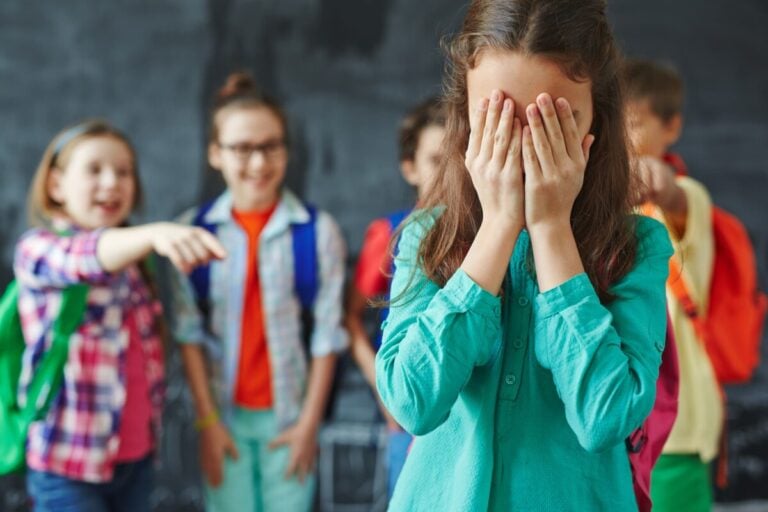

According to this logic, short arguments and occasional disagreements do not count as bullying. Although the intervention of teachers and educators is necessary in such situations, it is important to know how to distinguish “normal” problems from bullying. Bullying has no specific source.
Basically, a minor is intimidated or bullied, experiences verbal and physical aggression from the aggressor leader and a group of classmates who humiliate, blackmail, joke and exclude him from the class group.
A teenager who has become a victim receives aggression from the group publicly and endures it individually and anonymously. He does not turn to adults or peers for help, as threats are directed at him. He experiences this moment with sadness, anger, fear, guilt and shame. He withdraws into himself and separates himself from other classmates.
There is no uniform protocol in the education system that defines the rules to follow in the event of bullying at school. It is important to be able to distinguish school misunderstandings from bullying, which has extremely negative consequences.
Bullying at school – how does it manifest itself?
Bullying can take many forms and the bully may exhibit different behaviors towards the victim.
Verbal bullying:
- insult;
- name calling;
- curses;
- mockery;
- derogatory nicknames;
- offensive jokes.
Physical intimidation:
- hits/beatings;
- kicks;
- pushing;
- injury with a sharp object;
- theft or damage to the victim’s property;
- throwing objects at the victim.
Psychological abuse:
- humiliation;
- ridicule;
- insulation;
- ignoring;
- contempt;
- discrimination;
- threats;
- intimidation
- blackmail
- spreading rumors and intrigue.
Sometimes bullying can also be sexual in nature. This most often occurs with young people who use insults, coercion, harassment or sexual innuendo towards their victim in high school.
How can you tell if a child is being bullied?
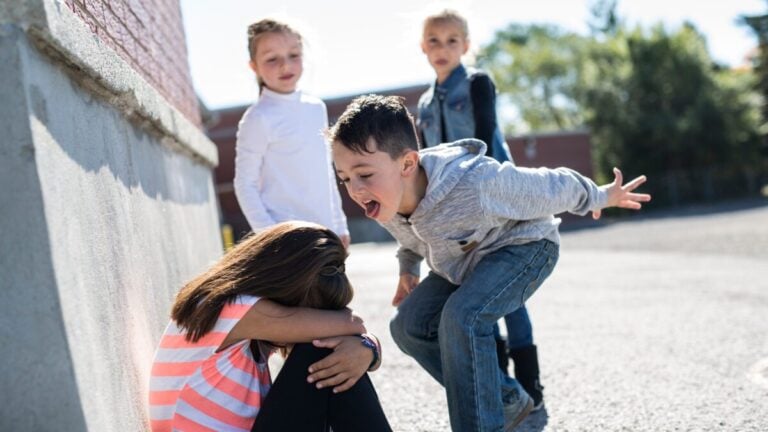

The most popular student in the class, attacks his classmate in the presence of other students, even in the presence of teachers. Those children who observe the situation support the leader and help him plan his aggressive actions. They encourage him to be verbally aggressive in public, which unfortunately can develop into physical aggression in the future.
Each manifestation of violence is perceived by the group as an achievement and strengthens the leadership of the aggressor in the class. This cements his or her role as a leader and a bully, which most members of the group agree with. The victim lives with shame and cannot defend himself. She feels humiliated, alone in this whole situation and guilty that she cannot stop the acts of humiliation she receives.
Victims of bullying find it difficult to explain what is happening to them, both at home and at school, due to fear of retaliation from peers. It is worth noting that children who are bullied exhibit symptoms that can be detected early at home.
These include:
- sleep problems or insomnia;
- loss or excessive appetite;
- reluctance to go to school;
- avoiding contact with peers;
- sudden changes in mood;
- refusal to give information about what is happening at school;
- does not talk about his classmates;
- calls or messages from school that the child suddenly felt physically unwell (headache, diarrhea, nausea, fainting);
- sadness;
- tearfulness;
- changes in grades and behavior at school.
It is important to remember that these are common symptoms of bullying when there is no physical or cognitive pathology that could explain them. It is worth contacting a psychologist to confirm your assumptions.
Bullying at school – who is the culprit and who is the victim?
The instigators of peer bullying are often people who themselves are struggling with internal problems. These may be students who feel misunderstood, have difficulty relating to others, or simply want to express their superiority in this way. They are often driven by the desire to gain recognition among other students by “using force” against weaker ones. There is also a group of offenders who have difficulty dealing with their own emotions and frustrations, which causes them to behave aggressively towards others.
Victims of bullying – why are they bullied?
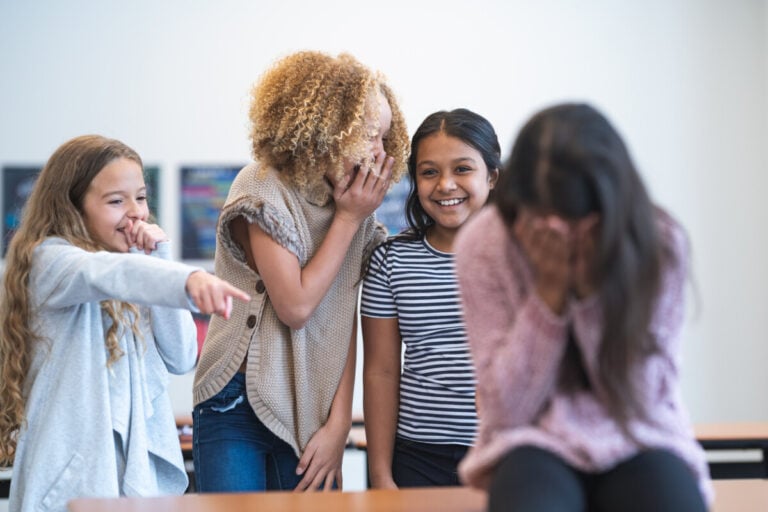

The typical target of bullying is a person who does not fit into the social norms considered “normal.” The reasons can be different: physical, psychological or behavioral. As a rule, aggressors choose as victims those who are different from themselves, those who are weaker, those who stand out from society in some way.
The most common victims of bullying are:
- Children who are overweight or too thin;
- Short or very tall;
- Does not fit into the standards of beauty imposed by society;
- With a lower socio-economic status;
- With learning difficulties;
- Low self-esteem;
- Very shy;
- Excellent students who have excellent academic performance, thereby causing envy and revenge among less diligent students.
Victims of bullying often suffer from low self-esteem, which makes it even more difficult for them to confront their bullies.
Understanding the mechanisms underlying school bullying and the characteristics of perpetrators and victims is key to effectively addressing bullying in school settings. This knowledge allows for more informed interventions to prevent bullying and support victims.
Victim of bullying – how can family help?
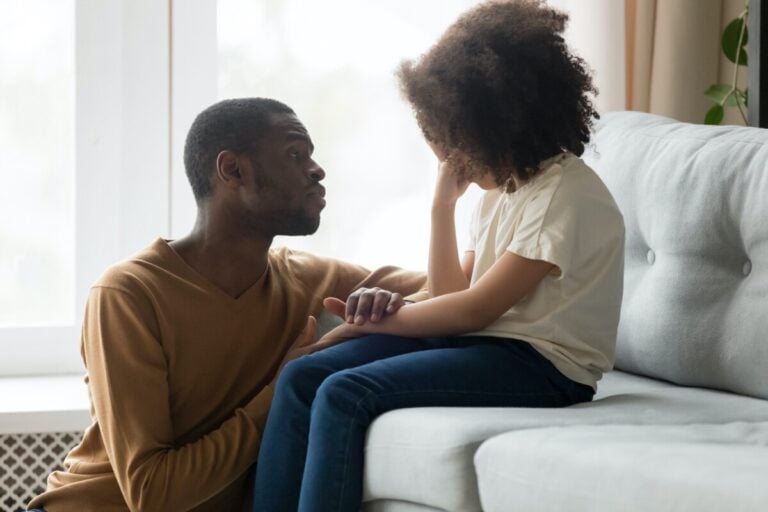

Parents can maintain open communication and dialogue with their children. It is worth talking with children often, listening and asking questions about school and relationships with peers. Children should be encouraged to report bullying to adults they trust (eg parents, teacher, psychologist). Even if parents are not able to directly solve the problem, they can console, support and advise.
If a child admits to being a victim of bullying or abuse, it is important not to ignore the situation. It is worth organizing a meeting with the class teacher, principal and school psychologist to find a joint solution.
Where should I go for help in case of bullying?
Psychologists often meet parents in their offices who are stunned by the situation when their children are being bullied by their peers. Parents report sudden changes in their children after they are bullied, harassed or excluded by their peers.
A victim does not have to have been bullied for a long time to begin psychological therapy. Sometimes just a few episodic acts of aggressive behavior in a group can meet all the necessary criteria to become a manifestation of the experience of bullying. For help, you can contact a school psychologist or, more conveniently, a psychological counseling center. Online consultations with a psychologist are also possible.